Web scraping for ecommerce helps businesses understand how marketplaces really behave over time. In fast-moving environments shaped by pricing changes, campaigns, and seller volatility, static reports are rarely enough. This guide explains how ecommerce web scraping transforms raw marketplace signals into reliable competitive insight.
What Is Web Scraping for Ecommerce
At a basic level, web scraping refers to the automated collection of publicly available data from websites. However, web scraping for ecommerce is not simply about extracting content from online stores or marketplaces.
Ecommerce data has several characteristics that make it fundamentally different:
- Dynamic pricing driven by campaigns, vouchers, and flash sales
- Campaign-centric behavior that temporarily reshapes rankings and visibility
- High seller and SKU volatility, especially in competitive categories
Because of these dynamics, one-off data snapshots rarely reflect how a market truly operates. Web scraping for ecommerce focuses on continuity, allowing teams to see patterns across time rather than isolated moments.
A common misconception is treating ecommerce scraping as a one-time data grab. In reality, its value comes from repeated observation and structured comparison (something manual checks and built-in dashboards are not designed to support).
Why Ecommerce Businesses Rely on Web Scraping
Ecommerce teams don’t adopt web scraping because they lack access to data. They adopt it because existing data sources fail to explain market behavior. This explains why ecommerce web scraping is increasingly viewed as an analytical foundation rather than a technical add-on.

Pricing Intelligence in Campaign-Driven Markets
In marketplaces dominated by promotions, headline prices often hide the real pricing strategy. Web scraping for ecommerce makes it possible to track base prices separately from vouchers and discounts, revealing whether competitors are structurally repricing or merely running short-term campaigns.
This is where competitive price monitoring and ecommerce use cases clearly demonstrate the practical value of ecommerce web scraping, especially for teams operating in highly promotional environments.
Category Saturation and Seller Density
Dashboards show what is currently listed. Scraped data shows how fast categories are filling up, how frequently new sellers appear, and whether competition is intensifying or stabilizing.
Assortment Gaps and Demand–Supply Imbalance
By observing listing growth alongside pricing and availability, ecommerce teams can identify gaps where demand outpaces supply (insights that rarely surface in internal sales data alone).
Monitoring Competitive Moves Before Sales Peaks
Repeated scraping helps teams spot early signals such as gradual price softening or inventory buildup (before major campaigns begin).
How to Get Marketplace Data Using Web Scraping
Getting marketplace data through web scraping is often described as a simple pipeline. In practice, the power of web scraping for ecommerce lies in how each step is aligned with market behavior, not in the mechanics alone.
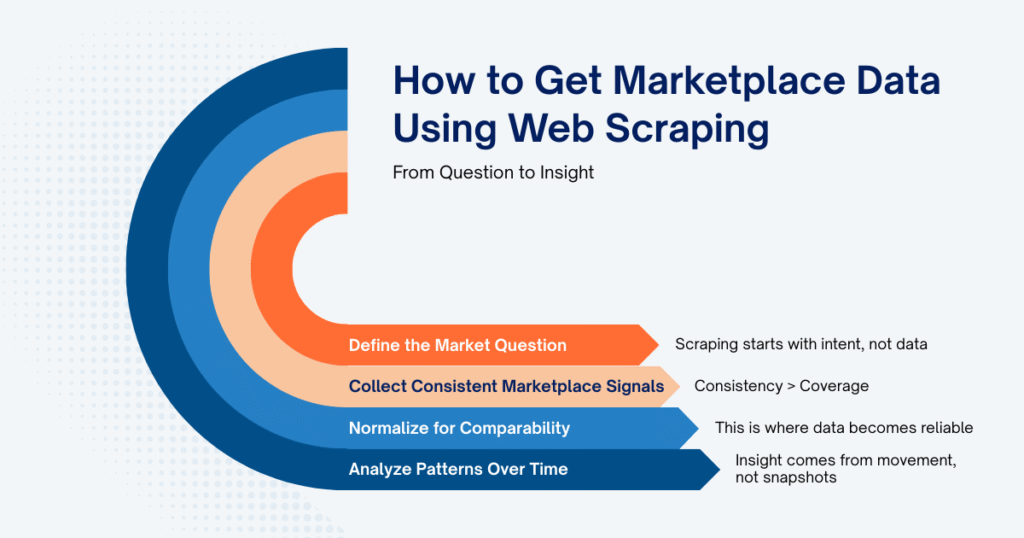
Defining the Market Question First
Web scraping rarely fails because of technical issues. It fails when teams start collecting data without knowing what they want to observe. Before scraping begins, effective ecommerce teams define:
- The market behavior they want to understand (pricing pressure, seller entry, demand signals)
- Which marketplace surfaces best reflect that behavior (categories, keywords, product listings)
- The time horizon over which the signal becomes meaningful
At this stage, web scraping for ecommerce acts as a market lens, shaping what data is collected and what is intentionally excluded.
Collecting Consistent Marketplace Signals
Once the scope is defined, scraping focuses on consistency rather than coverage. Instead of crawling everything, teams collect:
- The same page types
- With the same parameters
- At controlled intervals
This discipline ensures that scraped ecommerce data reflects how the marketplace presents itself over time, rather than a random aggregation of pages influenced by campaign noise.
Normalizing Data for Comparability
Raw marketplace data is unstable by nature. Prices shift, promotions stack, sellers duplicate listings, and layouts change. Normalization is where web scraping for ecommerce transitions from extraction to insight. At this stage, teams align:
- Price formats and promotional mechanics
- Product identifiers across sellers
- Category and keyword context
Without normalization, scraped data remains descriptive. With it, the data becomes analytically reliable.
Analyzing Patterns Across Time
Only after definition, collection, and normalization does analysis truly begin. Here, ecommerce teams focus on:
- Directional trends rather than point values
- Repeated patterns rather than anomalies
- Relationships between pricing, seller behavior, and visibility
This is where web scraping for ecommerce delivers its real advantage: enabling comparative, time-based analysis that supports confident decision-making.
Tools & Approaches for Web Scraping in Ecommerce
The choice of scraping tools often reflects how central marketplace data is to business decisions, not just technical preference.
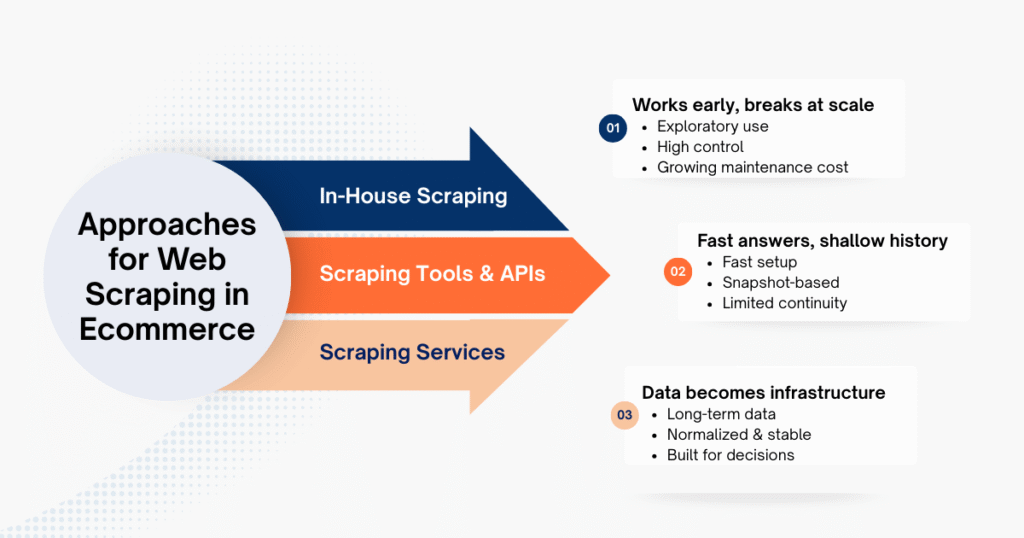
In-House Scraping: Control with Growing Overhead
Building internal scrapers offers maximum control and flexibility. This approach works well when web scraping for ecommerce supports short-term exploration or learning. However, as scraping becomes recurring, maintenance effort increases often more quickly than expected.
Scraping Tools: Speed and Accessibility
Off-the-shelf tools reduce setup time and technical friction. They are useful when speed matters more than depth or historical continuity. However, many are snapshot-oriented, requiring additional work before data becomes suitable for long-term analysis.
Professional Scraping Services: When Data Becomes Infrastructure
When ecommerce insights depend on stable, long-term data, scraping becomes infrastructure rather than a task. At this stage, reliability, normalization, and continuity matter more than setup speed.
This shift often marks a turning point in how web scraping for ecommerce is operationalized within an organization.
When Ecommerce Teams Move from Tools to Professional Web Scraping Services
Ecommerce teams typically start with scripts or tools. Over time, friction accumulates:
- Campaign-driven layout changes
- Data inconsistencies affecting benchmarks
- Increasing effort spent maintaining scrapers instead of analyzing markets
At this point, the key question is no longer how to scrape, but how to keep data trustworthy over time.
Professional services become relevant when scraped data feeds recurring decisions such as pricing strategy, category planning, or competitive monitoring.
How Easy Data Supports Scalable Web Scraping for Ecommerce
At Easy Data, ecommerce web scraping (including Shopee data scraping services, as well as TikTok and Lazada marketplaces) is designed around long-term analytical use rather than one-off extraction.
The service is built as a custom scraping setup, allowing businesses to define:
- What marketplace data to scrape
- Which countries and categories to cover
- How often data should be collected (daily, weekly, monthly, or during campaign windows)
Data is updated continuously and delivered in structured formats, enabling teams to focus on interpreting market signals instead of maintaining scraping systems.
With deep experience in Southeast Asia marketplaces, Easy Data emphasizes signal clarity over raw volume, helping teams reduce noise and improve decision confidence.
Conclusion
Web scraping for ecommerce has evolved from a technical tactic into a strategic capability. By enabling continuous observation of pricing, sellers, and demand, it fills critical gaps left by dashboards and manual reporting. When implemented with clear intent, consistent collection, and proper normalization, web scraping becomes a foundation for competitive insight rather than a data collection exercise.
Whether through in-house experimentation, scraping tools, or professional services, web scraping for ecommerce delivers the most value when it supports ongoing analysis, not isolated observation.


Leave a Reply