Definition of Web Scraping: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
In today’s data-driven world, the ability to extract valuable information from websites is crucial for businesses and researchers. Web scraping provides an efficient way to collect large volumes of data from websites. This data can be used for market research, competitor analysis, lead generation, and many other purposes. In this article, we will define what web scraping is, explain how it works, and discuss its importance in the modern digital landscape, particularly for e-commerce businesses that need up-to-date market data.
- Definition of Web Scraping: What Is It and Why Is It Important?
- What is Web Scraping?
- How Web Scraping Works
- Key Types of Web Scraping
- Applications of Web Scraping in E-commerce
- Advantages of Web Scraping
- Legal and Ethical Considerations in Web Scraping
- Conclusion: Understanding the Definition of Web Scraping and Its Benefits
What is Web Scraping?
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites using automated tools or scripts. These tools are designed to visit websites, interact with the content, and extract specific information like product listings, prices, reviews, and more. Web scraping can collect data from static pages, as well as dynamic content that requires JavaScript rendering.
The extracted data is then structured in a way that is useful for analysis or further processing, often in formats like CSV, Excel, JSON, or a database. Web scraping is widely used in various industries, including e-commerce, research, marketing, and finance, to gather insights from the web at scale.
For e-commerce businesses, scraping product data, competitor pricing, customer reviews, and more can provide a competitive edge in understanding market trends and consumer behavior.
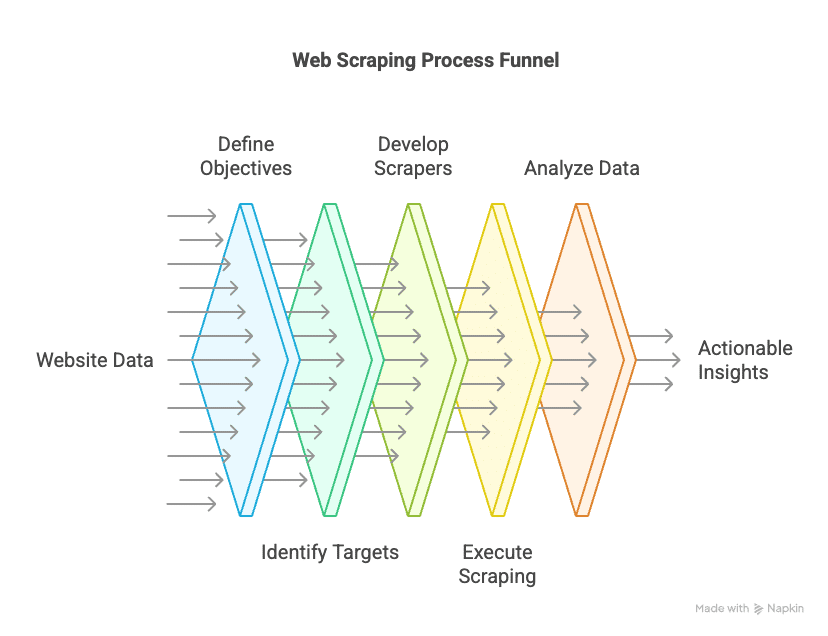
How Web Scraping Works
Web scraping typically involves the following steps:
- Send HTTP Request: The scraper sends an HTTP request to the website’s server to retrieve the HTML content of the web page.
- Parse the Content: The scraper then parses the HTML or XML content of the page to extract the relevant data. This is often done using libraries or frameworks such as BeautifulSoup (for Python) or Cheerio (for Node.js).
- Extract Data: Once the content is parsed, the scraper extracts the specific data points, such as text, links, images, or tables.
- Store the Data: The collected data is saved in a structured format for further use, such as analysis or integration into a database.
- Repeat: Many scraping tools are designed to scrape multiple pages or websites in one go. Some scrapers can handle pagination, infinite scroll, or even login credentials to gather data across entire websites.
Key Types of Web Scraping
-
Static Web Scraping
Static scraping refers to scraping data from static web pages, where the content doesn’t change dynamically. The data can be easily extracted using basic scraping tools or libraries, as the content is directly available in the page’s HTML. -
Dynamic Web Scraping
Dynamic scraping is required when extracting data from websites that rely on JavaScript or AJAX to load content. These websites dynamically generate or modify the content based on user interactions or data requests. Scraping dynamic websites often requires tools that can render JavaScript and capture the dynamically generated data. -
Screen Scraping
Screen scraping refers to the practice of extracting data by reading the screen output, typically from visual or graphical content. This method is often used when other scraping techniques are not possible. -
API Scraping
Some websites provide APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow developers to access structured data directly. While not technically “scraping” in the traditional sense, API scraping involves retrieving data from a website’s API endpoint, making it more efficient and reliable than scraping raw HTML content.
Applications of Web Scraping in E-commerce
Web scraping has numerous applications across various industries, particularly in e-commerce:
- Market Research: Web scraping allows businesses to monitor competitor prices, track market trends, and gather customer reviews. This helps companies make data-driven decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Lead Generation: Many businesses scrape data from online directories, job boards, and social media platforms to generate lists of potential leads or clients. Web scraping can automate the collection of contact details, company information, and job postings, reducing manual effort.
- E-commerce Price Monitoring: E-commerce businesses use web scraping to monitor product prices across different online stores. This allows them to adjust pricing strategies, track discounts, and ensure they remain competitive in the marketplace.
- Sentiment Analysis: Web scraping can be used to collect customer reviews and social media posts to analyze customer sentiment about a product, brand, or service. By analyzing large amounts of user-generated content, businesses can gain valuable insights into public opinion.
- Financial Market Data: In the financial industry, web scraping is used to collect real-time data on stock prices, company performance, and market news. This data is used by analysts, traders, and investors to make informed decisions.
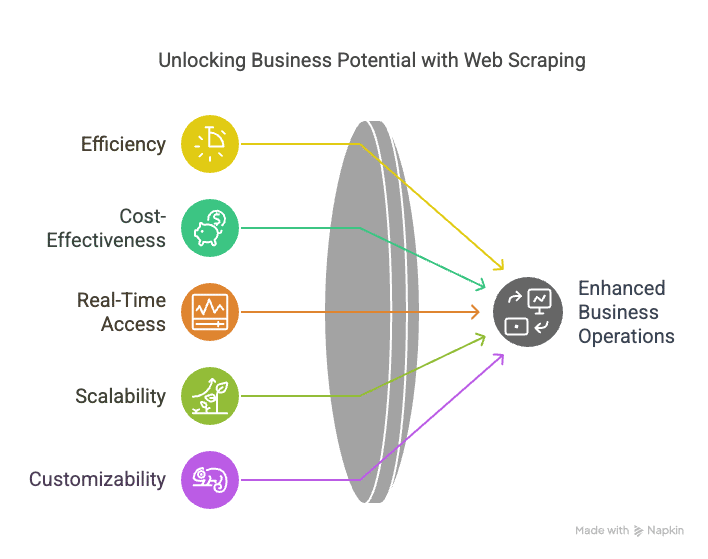
Advantages of Web Scraping
- Efficiency: Web scraping automates the process of data collection, saving businesses time and effort. It can gather large amounts of data in a short amount of time, which would be impossible manually.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional data collection methods, web scraping is much more affordable. It eliminates the need for purchasing third-party data or spending resources on manual data entry.
- Real-Time Access: Web scraping allows businesses to collect data in real-time, which is essential for tracking market trends, monitoring competitors, and making quick decisions.
- Scalability: Web scraping tools can be scaled to handle large amounts of data. Whether you’re scraping a small website or a massive online marketplace, scraping tools can handle the load efficiently.
- Customizable: Web scraping tools can be tailored to specific needs. You can configure the scraper to collect only the data you need and adjust it as your requirements evolve.
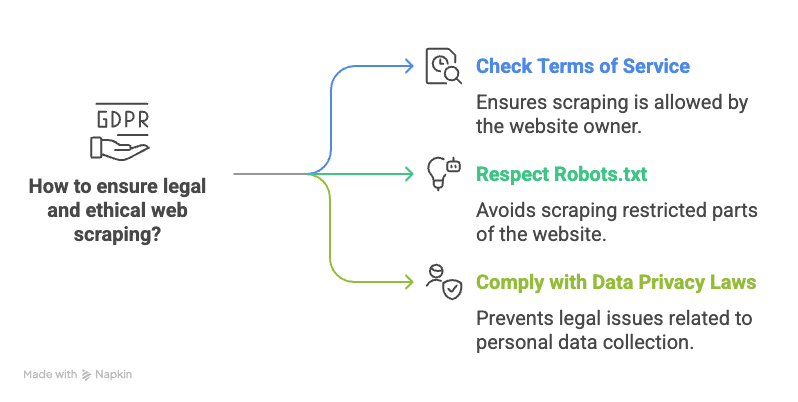
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Web Scraping
When collecting web scraping datasets, it’s essential to consider legal and ethical concerns:
- Website Terms of Service: Always review the terms of service for the websites you plan to scrape. Some websites prohibit scraping, and violating these terms can lead to legal consequences.
- Respect Robots.txt: Websites use robots.txt files to specify which parts of the site can be scraped. Make sure to respect these guidelines.
- Data Privacy: Ensure that you comply with data privacy laws such as GDPR when scraping personal data from websites.
Conclusion: Understanding the Definition of Web Scraping and Its Benefits
The definition of web scraping is simple, yet it encompasses a powerful technique that businesses can use to collect valuable data from websites. By automating the data extraction process, web scraping tools enable businesses to gather insights quickly, efficiently, and at scale. Whether you’re tracking competitor pricing, conducting market research, or generating leads, web scraping can give you the edge you need in today’s data-driven world, especially for e-commerce businesses that need timely market data to stay competitive.
For more information on how Easy Data can help with your web scraping needs, visit EasyData.io.vn.
External Links


Leave a Reply