Introduction
In the world of data extraction and automation, two commonly used techniques are Web Scraping vs Web Crawling. While both involve collecting data from websites, they serve different purposes and have distinct methodologies. Businesses looking to leverage big data, market research, and competitive intelligence must understand the differences between Web Scraping vs Web Crawling to choose the right approach.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of Web Scraping vs Web Crawling, their key differences, best practices, and how businesses can use them for growth.
For advanced web scraping and data collection solutions, visit Easy Data for expert insights and tools.

What is Web Crawling?
Definition of Web Crawling
Web Crawling is the process of systematically browsing the internet to collect, index, and store information from multiple websites. It is primarily used by search engines to discover and update web pages.
How Web Crawling Works
- A crawler (bot or spider) starts from a set of known web pages.
- It follows links on those pages to discover additional URLs.
- The data is indexed for future reference.
- The cycle repeats as new pages are found.
Common Use Cases of Web Crawling
- Search engine indexing (Google, Bing, and Yahoo! use crawlers to index web content).
- Monitoring website updates to track changes in competitors’ sites.
- Link analysis for SEO research and backlink audits.
- Data collection for AI training (natural language processing, content classification, etc.).
Web Crawling Tools
- Googlebot – Used by Google to crawl and index web pages.
- Screaming Frog – SEO-focused web crawler.
- HTTrack – A tool for offline website browsing.
What is Web Scraping?
Definition of Web Scraping
Web Scraping is the automated extraction of specific data from web pages. Unlike Web Crawling, which focuses on discovering new URLs, scraping extracts targeted content such as prices, text, or structured data.
How Web Scraping Works
- A scraper bot visits a website and loads the content.
- It extracts relevant data (e.g., product prices, stock information, articles).
- The extracted data is structured into a usable format (CSV, JSON, database).
- Businesses use the data for analysis, automation, or insights.
Common Use Cases of Web Scraping
- E-commerce price tracking to monitor competitors’ pricing.
- Market research to gather industry trends and customer sentiment.
- Lead generation by collecting business contacts.
- News aggregation by compiling articles from multiple sources.
- Real estate analysis to track property prices.
Web Scraping Tools
- BeautifulSoup – A Python library for parsing HTML and XML.
- Scrapy – A robust web scraping framework.
- Octoparse – A no-code web scraping tool.
Web Scraping vs Web Crawling: Key Differences
| Feature | Web Crawling | Web Scraping |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Discover and index web pages | Extract specific data |
| Focus | Finding new URLs and site structures | Collecting structured data |
| Use Case | Search engines, site monitoring | Data extraction for analytics, automation |
| Methodology | Following links across multiple sites | Targeting specific elements on a webpage |
| Output | List of URLs and metadata | Structured data (CSV, JSON, database) |
| Tools | Googlebot, Screaming Frog | BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, Octoparse |
Legal & Ethical Considerations
Both Web Scraping vs Web Crawling raise ethical and legal concerns. Websites often set rules through robots.txt files, and some protect content through CAPTCHAs and anti-scraping measures.
Best Practices for Ethical Data Collection
- Respect robots.txt rules – Check if a website allows crawling or scraping.
- Avoid overloading servers – Excessive requests can cause site slowdowns.
- Use APIs when available – Many platforms provide structured data access.
- Ensure compliance with data privacy laws – GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations.
For a deep dive into legal aspects and compliance, visit Easy Data for expert guidance.
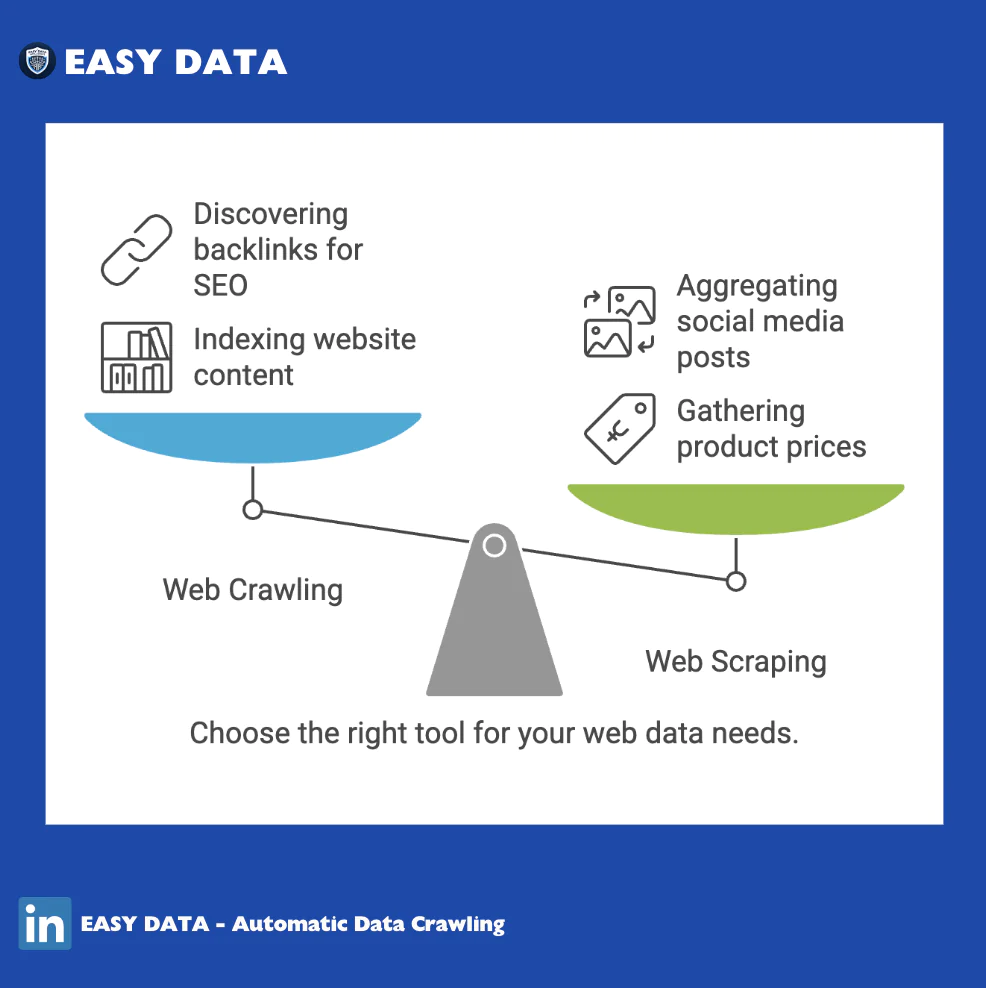
When to Use Web Crawling vs Web Scraping
| Scenario | Best Choice |
| Indexing website content | Web Crawling |
| Gathering product prices | Web Scraping |
| Discovering backlinks for SEO | Web Crawling |
| Extracting news headlines | Web Scraping |
| Monitoring website updates | Web Crawling |
| Aggregating social media posts | Web Scraping |
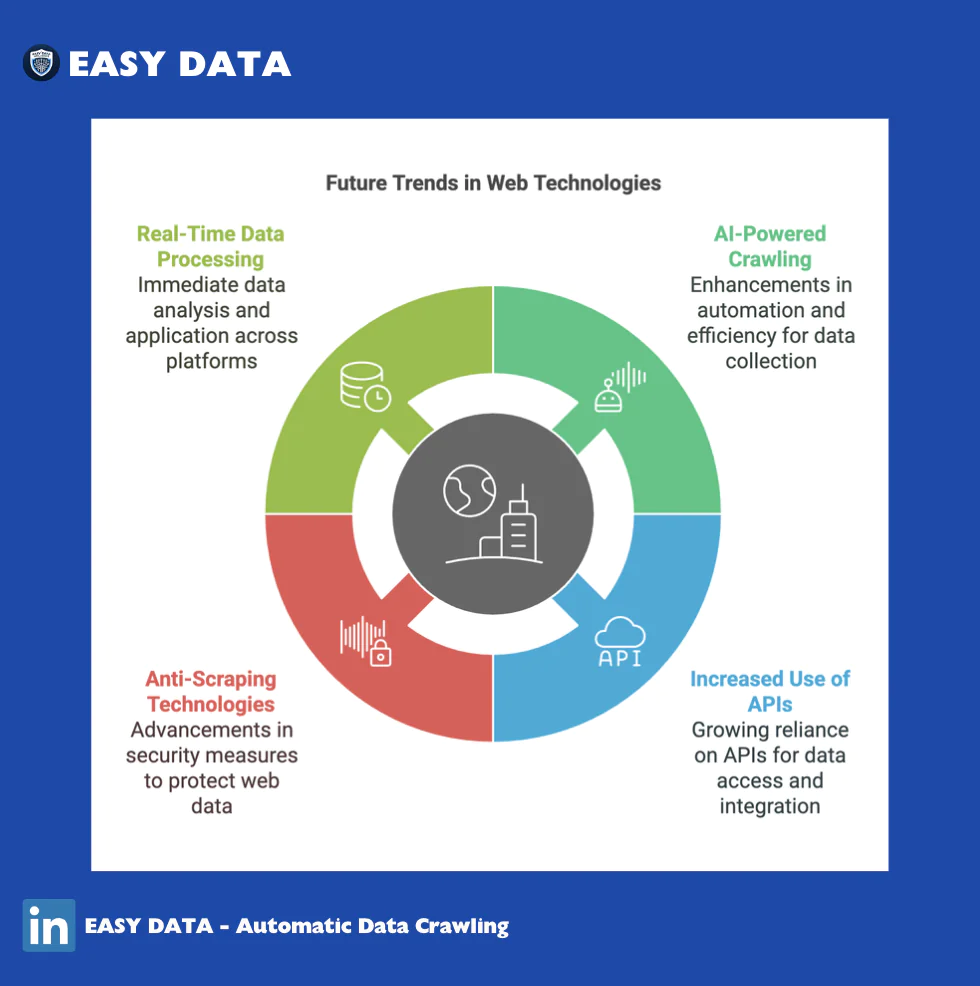
Future Trends in Web Scraping vs Web Crawling
1. AI-Powered Crawling and Scraping
- Machine learning is improving the accuracy of automated data extraction.
- AI-driven crawlers can prioritize high-value content.
2. Increased Use of APIs
- More companies are offering official APIs to reduce unauthorized data extraction.
- Businesses rely on API aggregators for structured data.
3. Anti-Scraping Technologies
- Websites are using CAPTCHAs, IP blocking, and JavaScript rendering to prevent scraping.
- Companies investing in ethical data collection strategies will gain long-term benefits.
4. Real-Time Data Processing
- Businesses demand real-time data feeds for market intelligence.
- Cloud-based scrapers can automate continuous data extraction.
Conclusion
Understanding Web Scraping vs Web Crawling is essential for businesses leveraging data extraction. While Web Crawling helps in discovering and indexing new content, Web Scraping is best for collecting specific data insights.
For businesses looking to extract high-quality, structured data, investing in efficient web scraping tools is crucial. Conversely, if the goal is to monitor web pages or index large datasets, then Web Crawling is the better approach.
For expert data collection strategies, automation, and compliance guidance, visit Easy Data.
For more insights on web data extraction, check out:


Leave a Reply