Introduction
E-commerce is transforming the way businesses and consumers interact, providing multiple avenues for trade across digital platforms. But what is types of e-commerce exactly? The term refers to the different business models within the online marketplace, including B2B, B2C, C2C, and emerging e-commerce trends like social commerce and subscription-based selling.
Understanding the types of e-commerce is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage digital sales and optimize their strategies. In this guide, we will explore the primary e-commerce models, their benefits, challenges, and future trends.
For real-time market insights and data-driven e-commerce solutions, visit Easy Data for expert analysis.
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-Commerce
What is B2C E-Commerce?
B2C e-commerce refers to businesses selling directly to consumers through online platforms. This model is the most common and includes everything from retail giants to small businesses.
Examples of B2C E-Commerce:
- Amazon, Shopee, Lazada – Multi-category online marketplaces.
- Nike, Apple, Samsung – Brands selling directly to consumers.
- ASOS, Zalora, Sephora – Fashion and beauty e-commerce stores.
Benefits of B2C E-Commerce:
- Global market reach and 24/7 accessibility.
- Lower operational costs compared to physical stores.
- Data-driven personalization through AI and analytics.
Challenges:
- High competition and customer acquisition costs.
- Logistics and order fulfillment complexities.
- Fraud risks and cybersecurity concerns.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B) E-Commerce
What is B2B E-Commerce?
B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses, such as wholesalers selling to retailers or manufacturers supplying raw materials to enterprises.
Examples of B2B E-Commerce:
- Alibaba & GlobalSources – International B2B marketplaces.
- Salesforce & HubSpot – Cloud-based SaaS providers.
- Uline & Grainger – Industrial and office supply businesses.
Benefits of B2B E-Commerce:
- Higher transaction values and long-term partnerships.
- Automation-driven efficiency in inventory and order management.
- Lower marketing costs compared to consumer markets.
Challenges:
- Complex negotiations and longer sales cycles.
- Requirement for bulk order fulfillment.
- Strict compliance with international trade regulations.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) E-Commerce
What is C2C E-Commerce?
C2C e-commerce allows consumers to sell directly to other consumers through peer-to-peer platforms.
Examples:
- eBay & Facebook Marketplace – General consumer resale platforms.
- Etsy & Depop – Handmade, vintage, and niche product marketplaces.
- Carousell & Poshmark – Second-hand and pre-owned goods.
Benefits:
- Low startup costs for sellers.
- Wide range of products and price flexibility.
- Sustainable shopping practices promoting second-hand sales.
Challenges:
- Payment security risks in peer-to-peer transactions.
- Limited scalability for individual sellers.
- Challenges with dispute resolution and product authenticity.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B) E-Commerce
What is C2B E-Commerce?
C2B e-commerce flips traditional business models by allowing consumers to offer products, services, or content directly to businesses.
Examples:
- Upwork & Fiverr – Freelance platforms where individuals offer services to companies.
- Shutterstock & Adobe Stock – Platforms where creators sell digital content.
- Influencer Marketing Networks – Brands hiring social media influencers for promotions.
Benefits:
- Gives individuals more control over pricing and services.
- Scalable earnings for freelancers and creators.
- Direct collaboration between brands and creators.
Challenges:
- Competitive market with pricing inconsistencies.
- Trust issues in contract fulfillment and payment security.
- Saturation of freelance services leading to price undercutting.
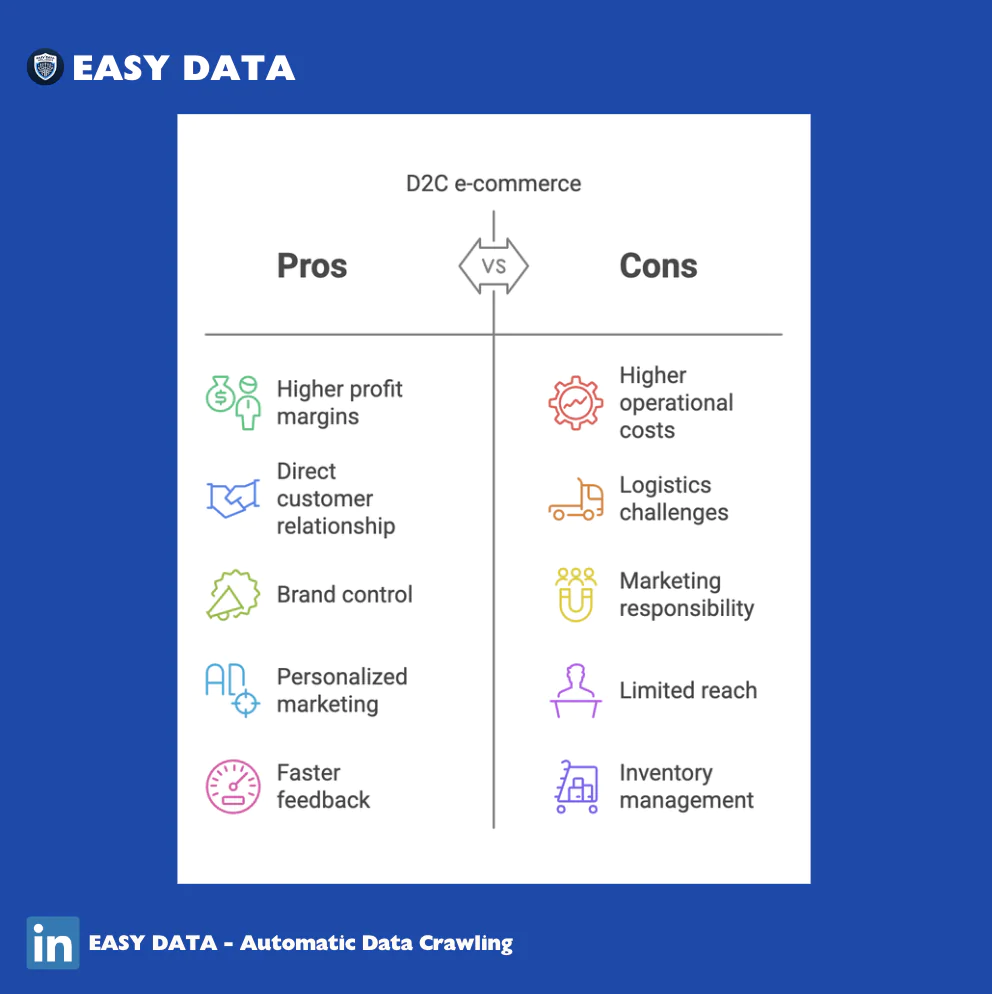
5. Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) E-Commerce
What is D2C E-Commerce?
D2C e-commerce involves brands selling directly to consumers without third-party intermediaries.
Examples:
- Tesla – Direct vehicle sales model.
- Warby Parker & Glossier – D2C lifestyle and beauty brands.
- Dollar Shave Club – Subscription-based direct sales.
Benefits:
- Higher profit margins by removing middlemen.
- Enhanced customer relationships and brand loyalty.
- Data-driven strategies for personalized marketing.
Challenges:
- Higher marketing and customer acquisition costs.
- Handling logistics, warehousing, and direct customer service.
- Scalability limitations compared to retail partnerships.
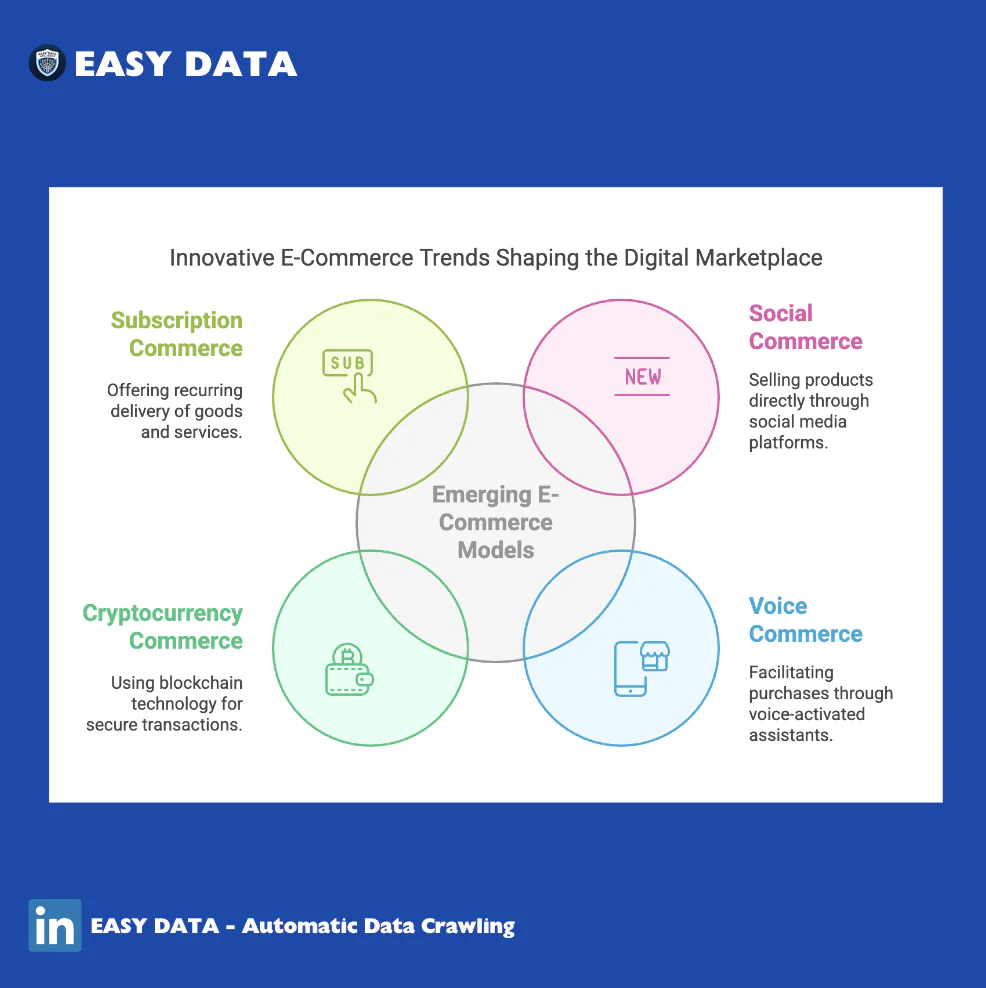
6. Emerging E-Commerce Models
With advancements in technology, new types of e-commerce are emerging:
- Social Commerce – Selling via social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and Facebook.
- Voice Commerce – Shopping through AI-powered voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant.
- Cryptocurrency-Based Commerce – Payments using blockchain technology.
- Subscription Commerce – Monthly recurring purchases like meal kits and streaming services.
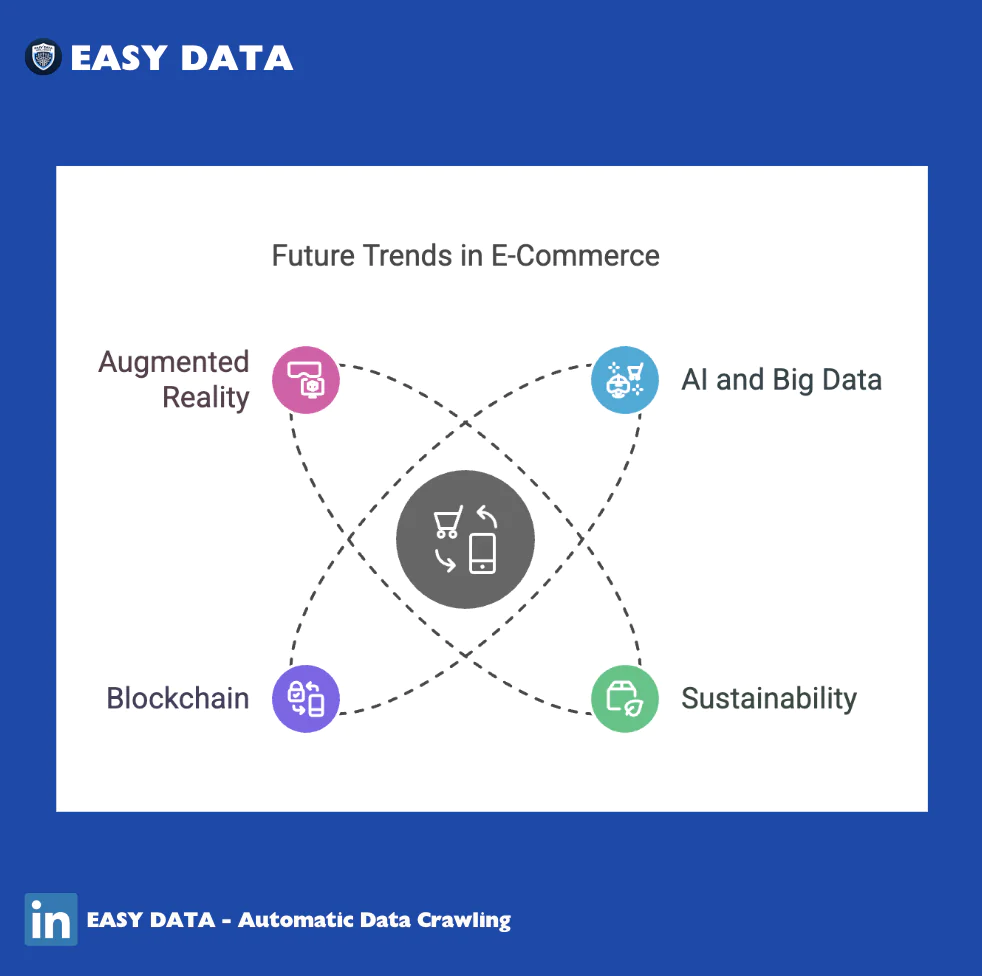
The Future of E-Commerce in 2025
As e-commerce continues to evolve, businesses must adapt to these trends:
- AI and big data will personalize shopping experiences.
- Sustainability will become a core focus in e-commerce logistics.
- Blockchain will enhance transaction security and transparency.
- Augmented reality (AR) will revolutionize online shopping experiences.
Conclusion
Understanding what is types of e-commerce helps businesses navigate the digital landscape effectively. Whether it’s B2B, B2C, C2C, C2B, or emerging trends, each model offers unique opportunities and challenges.
For businesses looking to scale their e-commerce strategies, leveraging data-driven insights is key. Visit Easy Data for the latest market trends, analytics, and e-commerce intelligence to stay ahead in the digital space.
For additional insights, check out Statista’s e-commerce research and Shopify’s latest e-commerce trends to stay updated with industry developments in 2025.


Leave a Reply