Introduction
The e-commerce industry is evolving rapidly, with multiple business models reshaping the digital marketplace. From B2B and B2C to C2C and D2C, understanding all types of e-commerce is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their online sales and scale globally.
This guide explores all types of e-commerce, their benefits, challenges, and future trends, offering valuable insights for businesses looking to expand their digital footprint.
For real-time e-commerce data and market insights, visit Easy Data for comprehensive analytics and growth strategies.
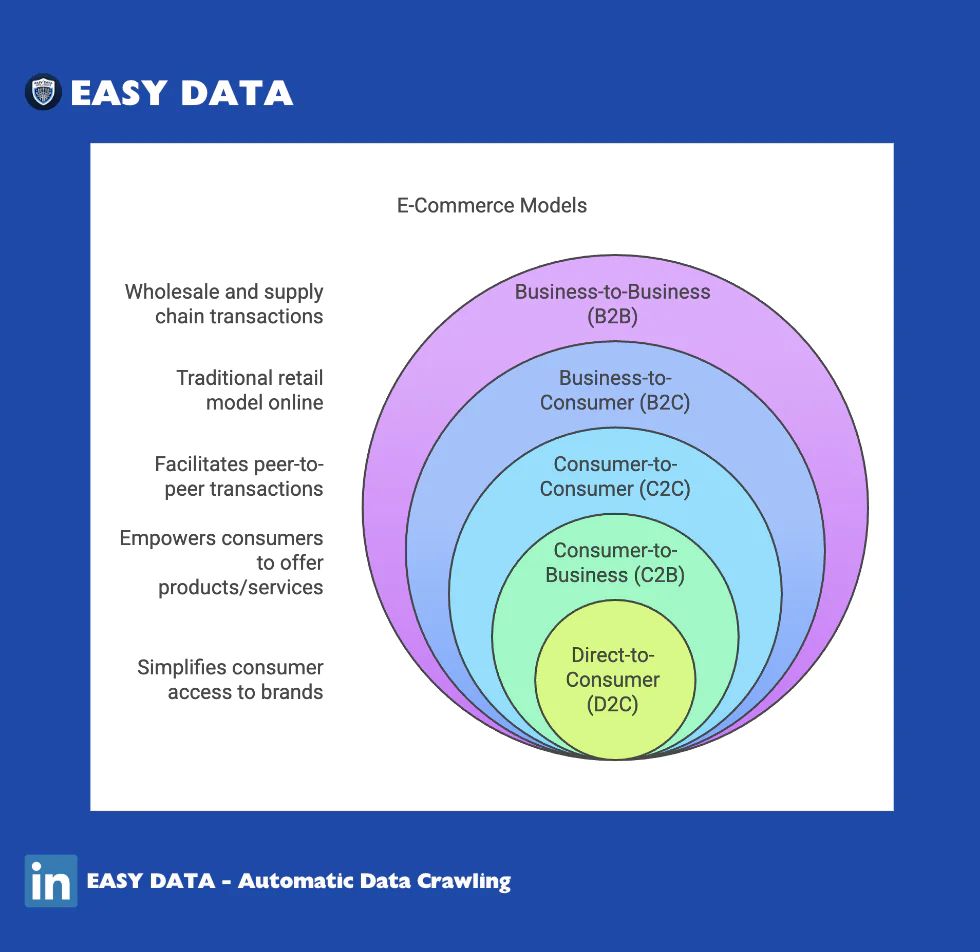
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-Commerce
What is B2C E-Commerce?
B2C e-commerce refers to businesses selling directly to consumers via digital platforms. This is the most common e-commerce model, covering everything from retail giants like Amazon and Shopee to small online boutiques.
Examples of B2C E-Commerce:
- Amazon, Shopee, and Lazada: Multi-category online marketplaces.
- Zalora & ASOS: Fashion-focused e-commerce platforms.
- Apple & Samsung Online Stores: Direct brand-to-consumer sales.
Benefits of B2C E-Commerce:
- Wide customer reach with global access.
- Lower operational costs compared to physical retail.
- Highly scalable with digital marketing strategies.
Challenges:
- High competition in saturated markets.
- Customer acquisition costs due to paid advertising reliance.
- Logistics and fulfillment complexities.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B) E-Commerce
What is B2B E-Commerce?
B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses, such as wholesalers selling to retailers or manufacturers supplying raw materials to industries.
Examples of B2B E-Commerce:
- Alibaba & GlobalSources: International B2B marketplaces.
- Salesforce & HubSpot: Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions.
- Uline & Grainger: Wholesale industrial suppliers.
Benefits:
- High-value transactions with recurring sales potential.
- Lower marketing costs due to long-term partnerships.
- Scalability with automation and AI-driven logistics.
Challenges:
- Longer sales cycles and complex negotiations.
- Trust and credibility concerns in international trade.
- Customization demands from enterprise clients.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) E-Commerce
What is C2C E-Commerce?
C2C platforms enable consumers to sell goods or services directly to other consumers, often through online marketplaces.
Examples:
- eBay & Facebook Marketplace: General C2C platforms.
- Etsy: Handmade and vintage goods.
- Depop & Carousell: Second-hand fashion and lifestyle goods.
Benefits:
- Low entry barriers for sellers.
- Diverse product selection.
- Sustainability benefits by promoting second-hand markets.
Challenges:
- Trust and security concerns with peer-to-peer transactions.
- Limited scalability for individual sellers.
- Payment and logistics handling challenges.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B) E-Commerce
What is C2B E-Commerce?
C2B reverses the traditional e-commerce model by allowing consumers to offer products, services, or content to businesses.
Examples:
- Fiverr & Upwork: Freelancers offering services to businesses.
- Influencer marketing platforms: Brands hiring social media influencers.
- Shutterstock & Adobe Stock: Digital content marketplaces.
Benefits:
- Flexible work opportunities for individuals.
- Scalable revenue models for freelancers and content creators.
- Direct brand collaboration without intermediaries.
Challenges:
- Pricing inconsistency based on market demand.
- High competition for freelancers and content creators.
- Trust issues with payment processing and intellectual property.
5. Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) E-Commerce
What is D2C E-Commerce?
D2C allows brands to sell directly to consumers, eliminating the need for third-party retailers or intermediaries.
Examples:
- Nike & Warby Parker: Brands with exclusive online stores.
- Dollar Shave Club & Glossier: Subscription-based D2C brands.
- Tesla: Direct sales model without dealerships.
Benefits:
- Higher profit margins by cutting out middlemen.
- Stronger brand control over messaging and customer relationships.
- Data-driven marketing with direct consumer insights.
Challenges:
- Marketing and acquisition costs without retailer partnerships.
- Customer support and logistics management.
- Scalability constraints for niche brands.
6. Emerging E-Commerce Models
Beyond the traditional models, new forms of e-commerce are emerging:
- Social Commerce: Selling through platforms like TikTok Shop, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Voice Commerce: Shopping via smart assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant.
- Subscription Commerce: Monthly product deliveries, such as meal kits and beauty boxes.
- Cryptocurrency-Based Commerce: Payments through Bitcoin and blockchain technology.
The Future of E-Commerce in 2025
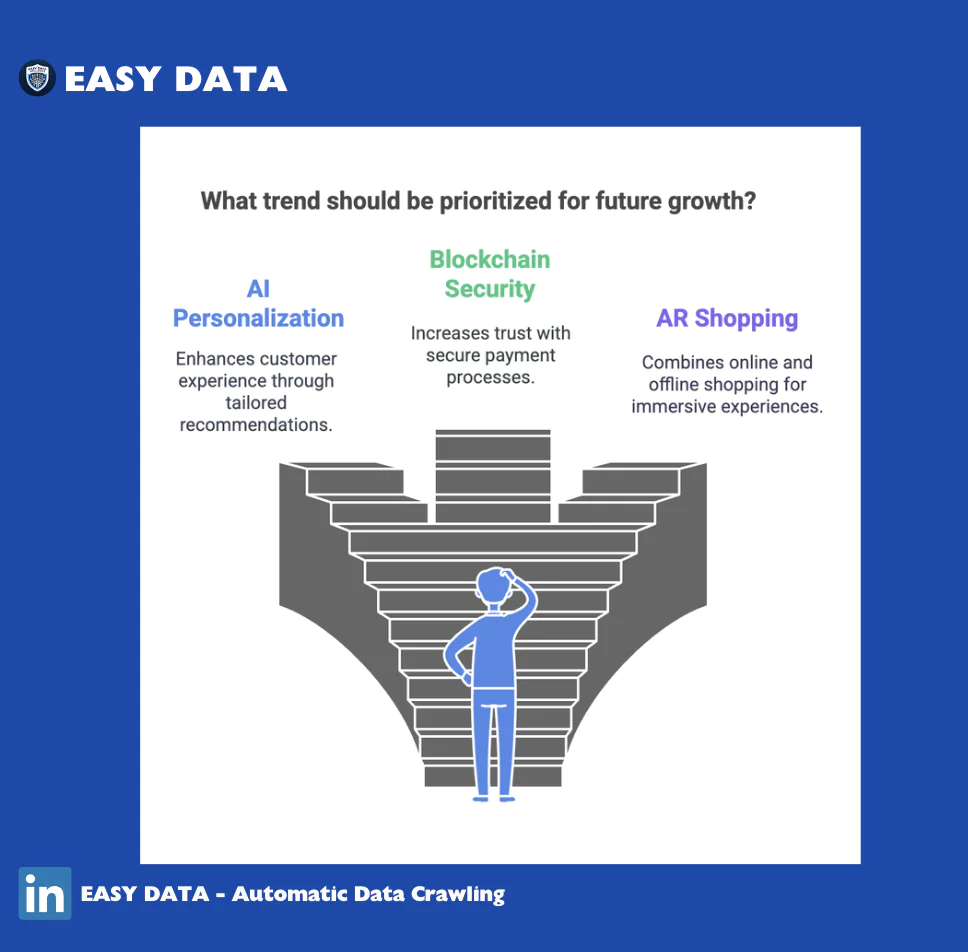
As e-commerce evolves, emerging trends will shape its future:
- AI-powered personalization will improve shopping experiences.
- Blockchain technology will enhance payment security.
- Augmented reality (AR) shopping will bridge online and offline experiences.
- Sustainability-driven commerce will encourage eco-friendly product choices.
Conclusion
Understanding all types of e-commerce is crucial for businesses and individuals entering the digital economy. Whether it’s B2B, B2C, C2C, D2C, or emerging models, each presents unique opportunities for growth.
For businesses looking to scale their e-commerce operations, leveraging data-driven insights is key. Visit Easy Data for the latest market trends, analytics, and e-commerce intelligence to stay ahead in the digital landscape.
For additional insights, check out Statista’s latest e-commerce report and Shopify’s e-commerce trends for industry developments in 2025.


Leave a Reply